Barsunova K, Vendelin M, Birkedal R
Sci Rep 2020 May;10(1):7956
PMID: 32409787
Abstract
Creatine kinase (CK) functions as an energy buffer in muscles. Its substrate, creatine, is generated by L-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT) and guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase (GAMT). Creatine deficiency has more severe consequences for AGAT than GAMT KO mice. In the present study, to characterize their muscle phenotype further, we recorded the weight of tibialis anterior (TA), extensor digi...
Read More
Papers
Cardiac muscle regulatory units are predicted to interact stronger than neighboring cross-bridges
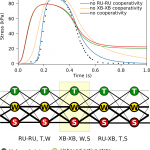
Kalda M, Vendelin M
Sci Rep 2020 Mar;10(1):5530
PMID: 32218497
Full text: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62452-7
Abstract
Model simulations (top) and the scheme showing cooperativity modes
Strong interactions between cross-bridges (XB) and regulatory units (RU) lead to a steep response of cardiac muscle to an increase in intracellular calcium. We developed a model to quantitatively assess the influence of different types of interactions within the sarcomere on the prope...
Read More
Energy-efficiency of Cardiomyocyte Stimulation with Rectangular Pulses
Laasmaa M, Lu P, Veletić M, Louch WE, Bergsland J, Balasingham I, Vendelin M
Sci Rep 2019 Sep;9(1):13307
PMID: 31527628
Abstract
In cardiac pacemaker design, energy expenditure is an important issue. This work aims to explore whether varying stimulation pulse configuration is a viable optimization strategy for reducing energy consumption by the pacemaker. A single cardiomyocyte was used as an experimental model. Each cardiomyocyte was stimulated with different stimulation protocols using rec...
Read More
Respiration of permeabilized cardiomyocytes from mice: no sex differences, but substrate-dependent changes in the apparent ADP-affinity
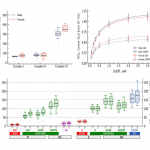
Karro N, Laasmaa M, Vendelin M, Birkedal R
Sci Rep 2019 Aug;9(1):12592
PMID: 31467353
Abstract
Sex differences in cardiac physiology are getting increased attention. This study assessed whether isolated, permeabilized cardiomyocytes from male and female C57BL/6 mice differ in terms of their respiration with multiple substrates and overall intracellular diffusion restriction estimated by the apparent ADP-affinity of respiration. Using respirometry, we recorded 1) the activities of respiratory...
Read More
IOCBIO Sparks detection and analysis software
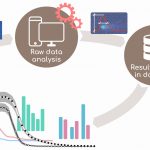
Laasmaa M, Karro N, Birkedal R, Vendelin M.
PeerJ. 2019 Mar 29;7:e6652
PMID: 30956900
Full text: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6652
Abstract
Analysis of calcium
sparks in cardiomyocytes can provide valuable information about
functional changes of calcium handling in health and disease. As a part
of the calcium sparks analysis, sparks detection and characterization is
necessary. Here, we describe a new open-source platform for automatic
calcium sparks detection from line ...
Read More
Revealing calcium fluxes by analyzing inhibition dynamics in action potential clamp
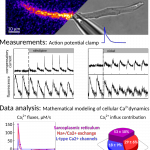
Laasmaa M, Birkedal R, Vendelin M
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. Volume 100, November 2016, Pages 93–108
PMID: 27702573
Full text: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.08.015
Abstract
In cardiac excitation-contraction coupling (ECC), calcium enters the cytosol via L-type Ca2+ channels (LTCC) and reverse Na+/Ca2+-exchange (NCXrev), or is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) by Ca2+-induced Ca2+-release (CICR). The magnitude of Ca2+ influx via the different pathways varies with the ...
Read More
Metabolic compartmentation in rainbow trout cardiomyocytes: coupling of hexokinase but not creatine kinase to mitochondrial respiration
Karro N, Sepp M, Jugai S, Laasmaa M, Vendelin M, Birkedal R
J. Comp. Physiol. B, Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2016 Aug;
PMID: 27522222
Full text: http://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-1025-x
Abstract
Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cardiomyocytes have a simple morphology with fewer membrane structures such as sarcoplasmic reticulum and t-tubules penetrating the cytosol. Despite this, intracellular ADP diffusion is restricted. Intriguingly, although diffusion is restricted, trout cardiom...
Read More
Restricted ADP movement in cardiomyocytes: Cytosolic diffusion obstacles are complemented with a small number of open mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channels
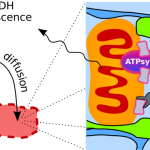
Simson P, Jepihhina N, Laasmaa M, Peterson P, Birkedal R, Vendelin M
J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. Volume 97, August 2016, Pages 197–203;
PMID: 27261153
Full text: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.04.012
Abstract
Adequate intracellular energy transfer is crucial for proper cardiac function. In energy starved failing hearts, partial restoration of energy transfer can rescue mechanical performance. There are two types of diffusion obstacles that interfere with energy transfer from mit...
Read More
Cross-Bridge Group Ensembles Describing Cooperativity in Thermodynamically Consistent Way
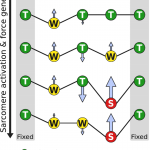
Kalda M, Peterson P, Vendelin M
PLoS ONE 2015;10(9):e0137438
PMID: 26361396
Full text: http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137438
Abstract
The aim of this work is to incorporate cooperativity into Huxley-type cross-bridge model in thermodynamically consistent way. While the Huxley-type models assume that cross-bridges act independently from each other, we take into account that each cross-bridge is influenced by its neighbors and cooperativity is induced by tropomyosin movement. For that...
Read More
The location of energetic compartments affects energetic communication in cardiomyocytes
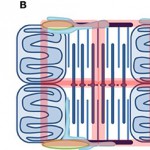
Birkedal R, Laasmaa M, Vendelin M
Front Physiol 2014;5:376
PMID: 25324784
Full text: http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2014.00376
Abstract
The heart relies on accurate regulation of mitochondrial energy supply to match energy demand. The main regulators are Ca(2+) and feedback of ADP and Pi. Regulation via feedback has intrigued for decades. First, the heart exhibits a remarkable metabolic stability. Second, diffusion of ADP and other molecules is restricted specifically in heart an...
Read More